
Individuals who struggle with nasal congestion, cough, facial pressure/pain, purulent nasal drainage and headache may have rhinosinusitis, commonly termed sinusitis.
The sinuses are air spaces or holes in the face and head. They are lined with nasal mucosa but should be full of air. The passages that drain the sinuses are quite small and when something blocks these drainage pathways, infection can occur.
Obstruction of the nasal drainage pathways can cause both acute and chronic sinusitis. Acute sinusitis lasts less than four weeks and most cases begin with a common cold. While most cases resolve in their own, occasionally the sinuses can become secondarily infected with bacteria and need antibiotics. Chronic sinusitis lasts for 12 weeks or longer.
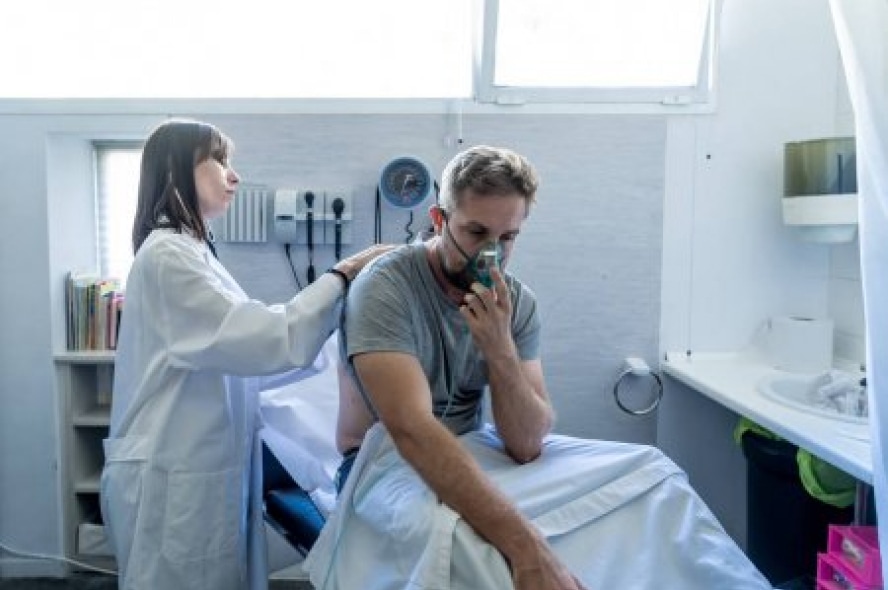
Asthma causes recurrent symptoms of coughing, wheezing, chest tightness or shortness of breath. Symptoms often occur with activity or are triggered by certain exposures such as extreme cold or hot temperature, smoke, fumes, pollen, allergens (like pets or dust) or infections.
If you have asthma, an allergist may perform lung function testing, also called spirometry, to monitor your lung function over time and guide treatment. Other tests may also be ordered to help identify triggers to your symptoms with skin testing.
Medications used to treat asthma include short acting bronchodilators (like albuterol) for acute symptoms and maintenance medications like inhaled corticosteroids or leukotriene receptor modifiers. Allergists use these medications to decrease airway inflammation along with identifying and avoiding triggers to help improve symptoms. Sometimes, asthma that is severe or very difficult to control, needs further controller therapy with biologics. These are injectable medications that are used to treat certain kinds of asthma. Often, these medications require a blood test to determine which one is most appropriate.
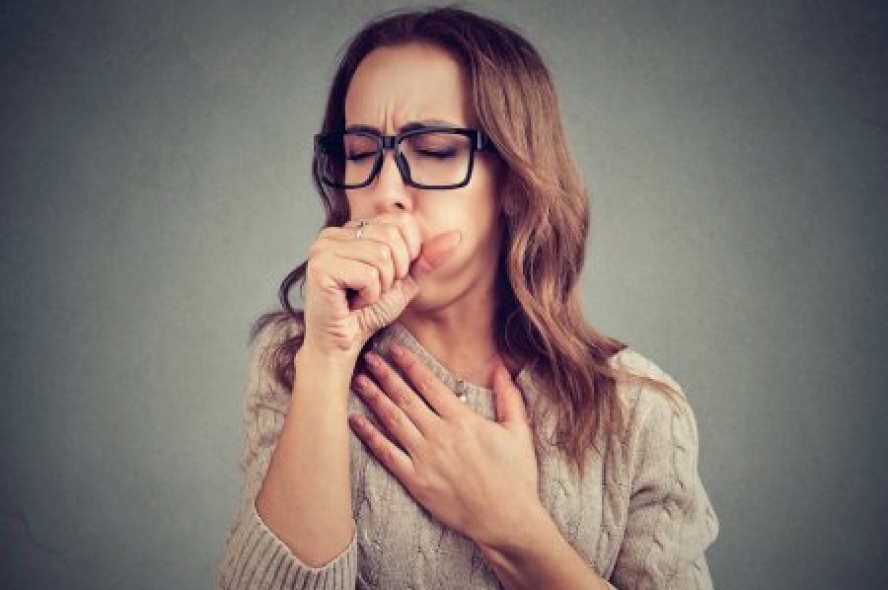

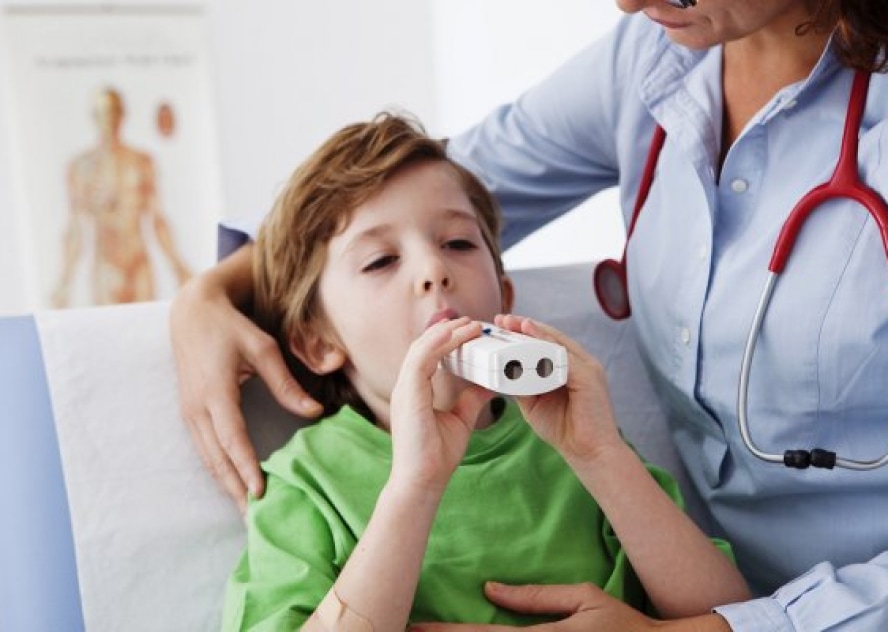
The goal for all asthmatics is to use the lowest amount of medication to control the symptoms, avoid exacerbations that lead to hospitalizations or missed work/school days, and enjoy a healthy quality of life.
An allergist/immunologist is the best qualified physician in diagnosing and treating asthma. With the help of your allergist, you can take control of your asthma and take control of your life.
